Pharma - Water purification
Pure water, or better still, the purest water, is the most widely used raw material in the pharmaceutical industry. Terms such as "Purified Water" (PW), "Ultra Pure Water" (UPW) or "Water For Injection" (WFI) are widely known in this sector.
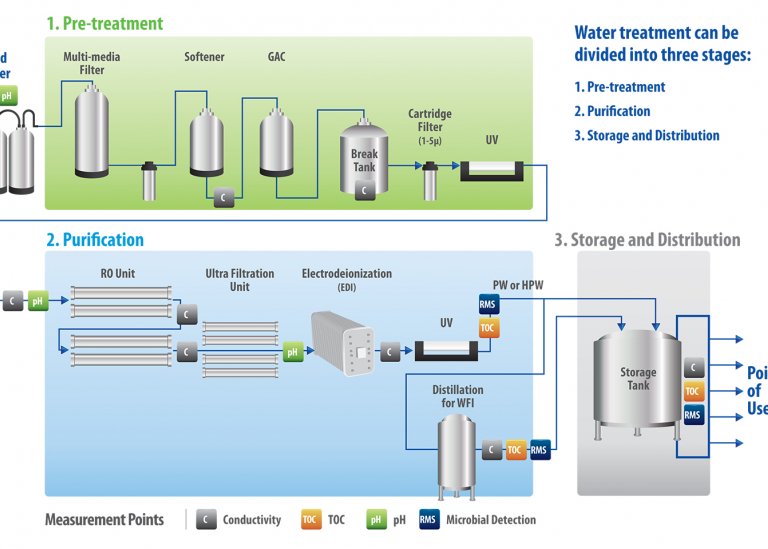
That pure water doesn’t just come from the tap, you have to make it. Starting from drinking water quality, the water undergoes several purification steps, such as deionisation, distillation, reverse osmosis, (ultra) filtration, etc. During or after all these steps, the water quality is continuously monitored in real time. The key parameters are:
- Conductivity
- TOC
- Bioburden - RMS
- Ozone (O3)
- pH
Follow the guidelines of the International Pharmacopoeia
Almost every country has its own pharmaceutical organisation. Fortunately, the vast majority are aligned (harmonised). The main pharmacopoeias are the European (EP), the American (USP), the Chinese (ChP), the Japanese (JP) and the Indian (IP). Their manuals describe the criteria that the various parameters have to meet, how the measurements should be made and how to calibrate or verify the devices and analysers.
Conductivity measurement
Conductivity or conductance is just about the most measured parameter. It measures the total amount of conductive substances (ions, polar molecules, etc.). The very purest water has a conductivity of 0.055µS/cm at 25°C. Digital conductivity sensors have become indispensable because they are significantly more accurate than their traditional predecessors.
TOC analysis
Non-conductive, organic substances are determined with a "Total Organic Carbon" analyser. It is important to choose an analyser that continuously analyses the water and not one that periodically takes a sample and determines the TOC in it. You never know what can happen in a few minutes!
Bioburden – RMS
The only way to determine bacterial contamination is to measure it. A "Real-Time Microbial System" constantly analyses the water flow. Each individual bacterium is detected! These "Bioburden" analysers replace the expensive and time-consuming (up to more than 5 days) lab analysis.
Ozone
Ozone (O3), which is one of the most powerful oxidising agents, is used for disinfection. Every organic pollutant is converted to CO2. It also kills any micro-organisms that may be present. Ozone is not only a useful disinfectant, but also an undesirable substance in the WFI or PW that eventually ends up with the end user. The ozone concentration should therefore be measured before the ozone generator and after the UV destruction.
pH measurement
With a pH measurement we monitor the acidity of the water. Many contaminants already have an effect on the pH of the water in very low concentrations, so that a pH measurement reacts quickly. A pH measurement also monitors the proper functioning of various purification techniques such as ion exchangers. Make no mistake, pH measurement in pure water is one of the most difficult analytical measurements. It’s therefore best to use an electrode that’s specifically intended for this application.
More information?